Hypereosinophilia: A Guideline for Workup in the Allergy Community
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58931/cait.2022.2232Abstract
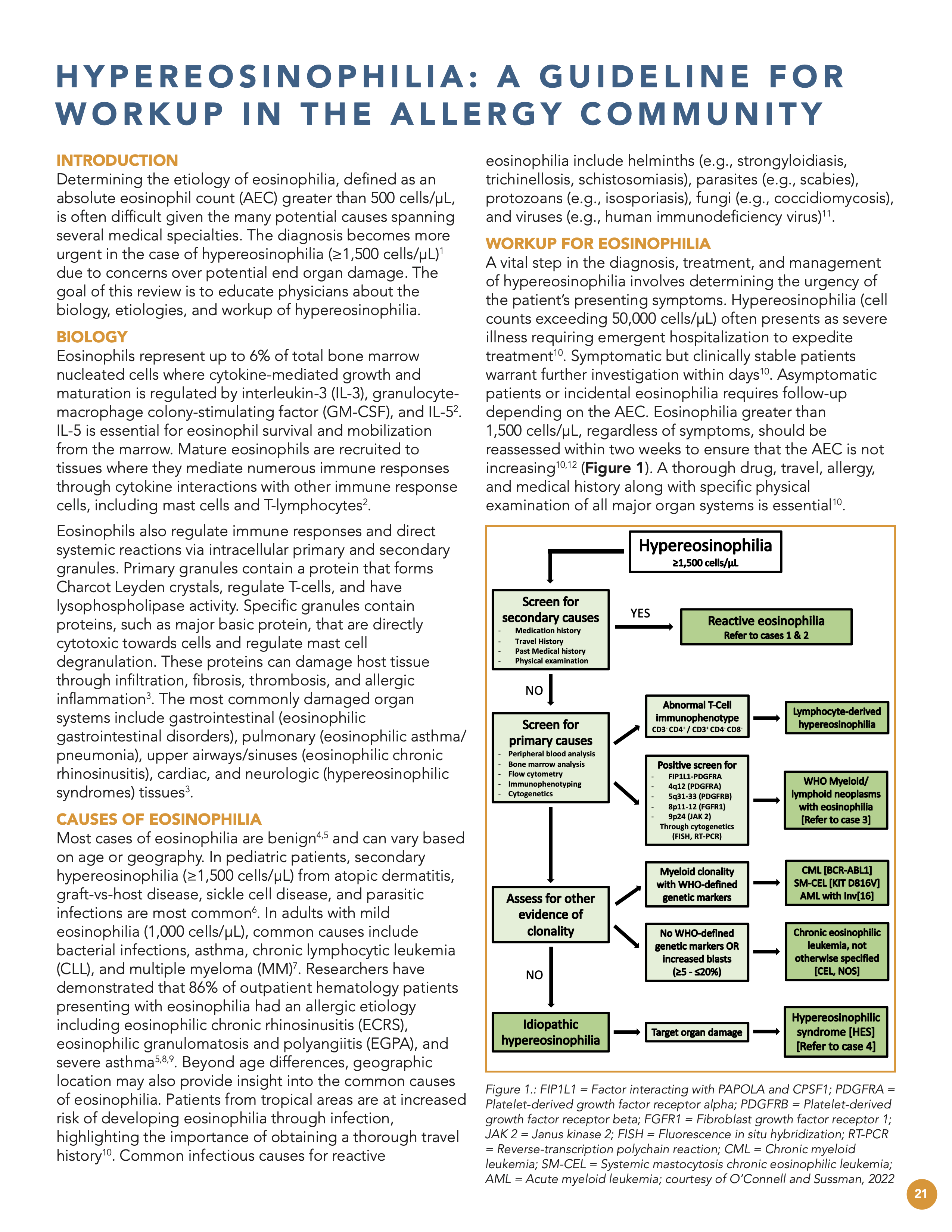
Determining the etiology of eosinophilia, defined as an absolute eosinophil count (AEC) greater than 500 cells/µL, is often difficult given the many potential causes spanning several medical specialties. The diagnosis becomes more urgent in the case of hypereosinophilia (≥1,500 cells/µL) due to concerns over potential end organ damage. The goal of this review is to educate physicians about the biology, etiologies, and workup of hypereosinophilia.
References
Chusid MJ, Dale DC, West BC, Wolff SM. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine. 1975 Jan;54(1):1-27.
Ramirez GA, Yacoub MR, Ripa M, et al. Eosinophils from Physiology to Disease: A Comprehensive Review. BioMed research international. 2018;2018:9095275. doi:10.1155/2018/9095275
Akuthota P, Weller PF. Spectrum of Eosinophilic End-Organ Manifestations. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2015;35(3):403-411. doi:10.1016/j.iac.2015.04.002
Magnaval J-F, Laurent G, Gaudré N, Fillaux J, Berry A. A diagnostic protocol designed for determining allergic causes in patients with blood eosinophilia. Military Medical Research. 2017 May 23;4(1):15. doi:10.1186/s40779-017-0124-7
Nelson RK, Bush A, Stokes J, Nair P, Akuthota P. Eosinophilic Asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol: In practice. 2020 Feb;8(2):465-473. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2019.11.024
Burris D, Rosenberg CE, Schwartz JT, et al. Pediatric Hypereosinophilia: Characteristics, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnoses. J Allergy Clin Immunol: In practice. 2019 Nov-Dec;7(8):2750-2758.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2019.05.011
Leverone N, Tran S, Barry J, Akuthota P. Diagnoses associated with peripheral blood eosinophilia: A 5-year review. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;127(5):597-598. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2021.08.013
Fujieda S, Imoto Y, Kato Y, et al. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergology international : official journal of the Japanese Society of Allergology. 2019 Oct;68(4):403-412. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2019.07.002
Reiter A, Gotlib J. Myeloid neoplasms with eosinophilia. Blood. 2017 Feb 9;129(6):704-714. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-10-695973
Butt NM, Lambert J, Ali S, et al. Guideline for the investigation and management of eosinophilia. Br J Haematol. 2017;176(4):553-572. doi:10.1111/bjh.14488
Roufosse F, Weller PF. Practical approach to the patient with hypereosinophilia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126(1):39-44. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2010.04.011
Stauffer WM, Alpern JD, Walker PF. COVID-19 and Dexamethasone: A Potential Strategy to Avoid Steroid-Related Strongyloides Hyperinfection. JAMA. 2020;324(7):623-624. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.13170
Haldar P, Brightling CE, Hargadon B, et al. Mepolizumab and Exacerbations of Refractory Eosinophilic Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(10):973-984. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0808991
Nair P, Pizzichini MM, Kjarsgaard M, et al. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 2009 Mar 5;360(10):985-93. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0805435
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016 May 19;127(20):2391-405. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544
Ault P, Cortes J, Koller C, Kaled ES, Kantarjian H. Response of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome to treatment with imatinib mesylate. Leuk Res. 2002 Sep;26(9):881-4. doi:10.1016/s0145-2126(02)00046-2
Cools J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, et al. A tyrosine kinase created by fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 genes as a therapeutic target of imatinib in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003 Mar 27;348(13):1201-14. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa025217
Gleich GJ, Leiferman KM, Pardanani A, Tefferi A, Butterfield JH. Treatment of hypereosinophilic syndrome with imatinib mesilate. Lancet. 2002 May 4;359(9317):1577-8. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08505-7
Schaller JL, Burkland GA. Case report: rapid and complete control of idiopathic hypereosinophilia with imatinib mesylate. MedGenMed: Medscape general medicine. 2001 Sep 7;3(5):9.
Stover EH, Chen J, Lee BH, et al. The small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor AMN107 inhibits TEL-PDGFRbeta and FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2005;106(9):3206-3213. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-05-1932
Nair P, Ochkur SI, Protheroe C, Simms E, Lee NA, Lee JJ. The identification of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in prednisone-dependent eosinophilic bronchitis and asthma. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology. 2011 Mar 1;7(1):4. doi:10.1186/1710-1492-7-4
Gioffredi A, Maritati F, Oliva E, Buzio C. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: an overview. Front Immunol. 2014;5:549-549. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00549
Bel EH, Wenzel SE, Thompson PJ, et al. Oral Glucocorticoid-Sparing Effect of Mepolizumab in Eosinophilic Asthma. New England Journal of Medicine. 2014;371(13):1189-1197. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1403291
Betancor D, Plaza KL, Eguez JC, Nair P, Trus M. Exon 8 KIT mutation and pulmonary eosinophilia. Allergy. 2020;75(8):2094-2096. doi:10.1111/all.14272